Large language model agents are starting to store what they see, but can they really improve their policies at the time of testing from those experiences rather than rerunning the context window?
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and Google DeepMind have proposed evo-memoryA streaming benchmark and agent framework that targets this exact gap. Evo-Memory Evaluates trial-time learning with self developing memoryAsking whether agents could accumulate and reuse strategies from a continuous work stream rather than relying solely on static conversation logs.
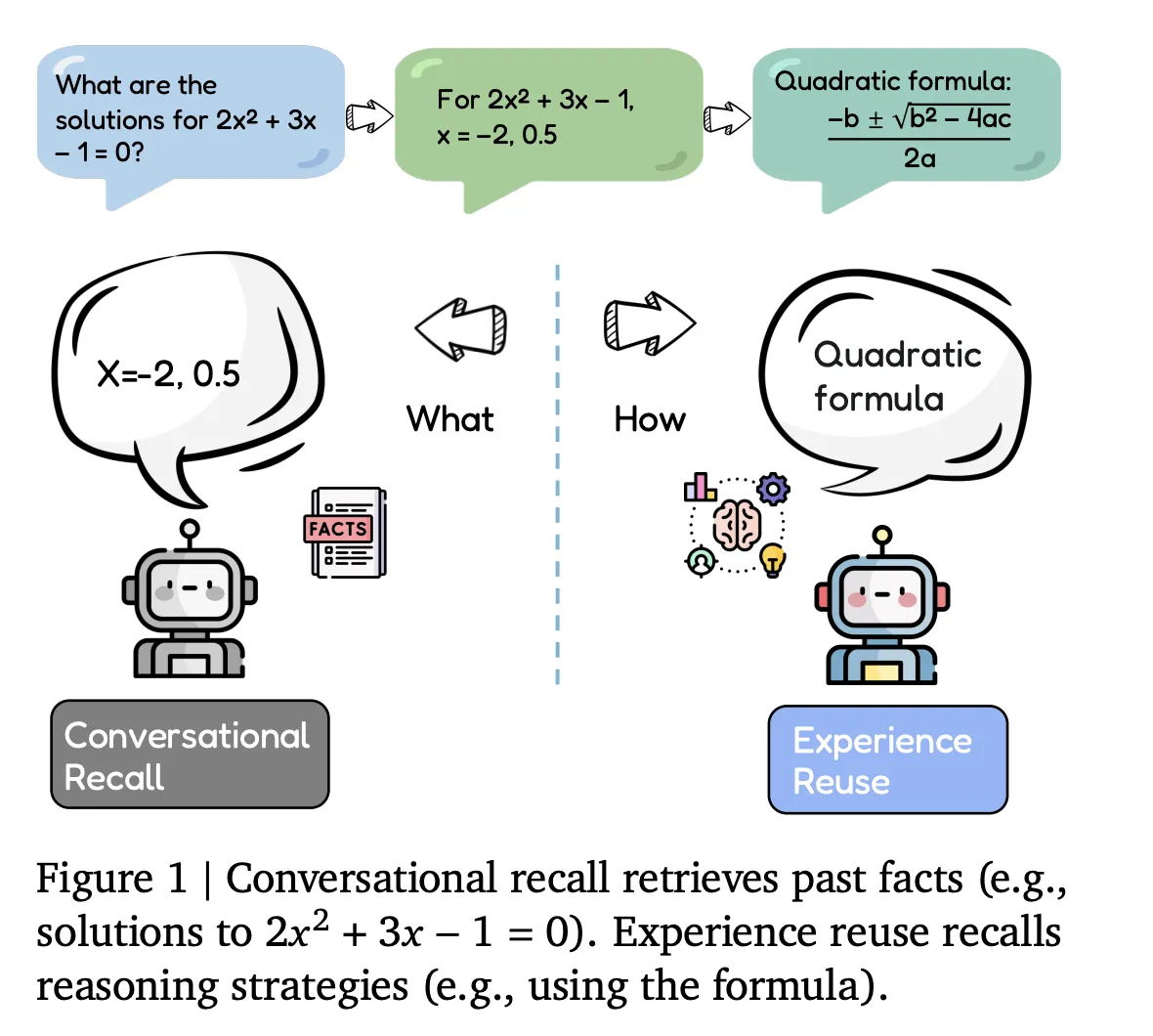
Conversational Recall vs. Experience Reuse
Most current agents implement conversational recallThey store dialogue history, tool traces, and retrieved documents, which are reintegrated into the context window for future queries, This type of memory acts as a passive buffer, capable of retrieving facts or recalling previous steps, but it does not actively modify the agent’s approach to the tasks in question,
Instead the focus is on evo-memory Experience ReuseHere each interaction is treated as an experience that encodes not only inputs and outputs, but also whether an action was successful and which strategies were effective, The benchmark tests whether agents can retrieve those experiences in subsequent tasks, apply them as reusable processes, and refine the memory over time,
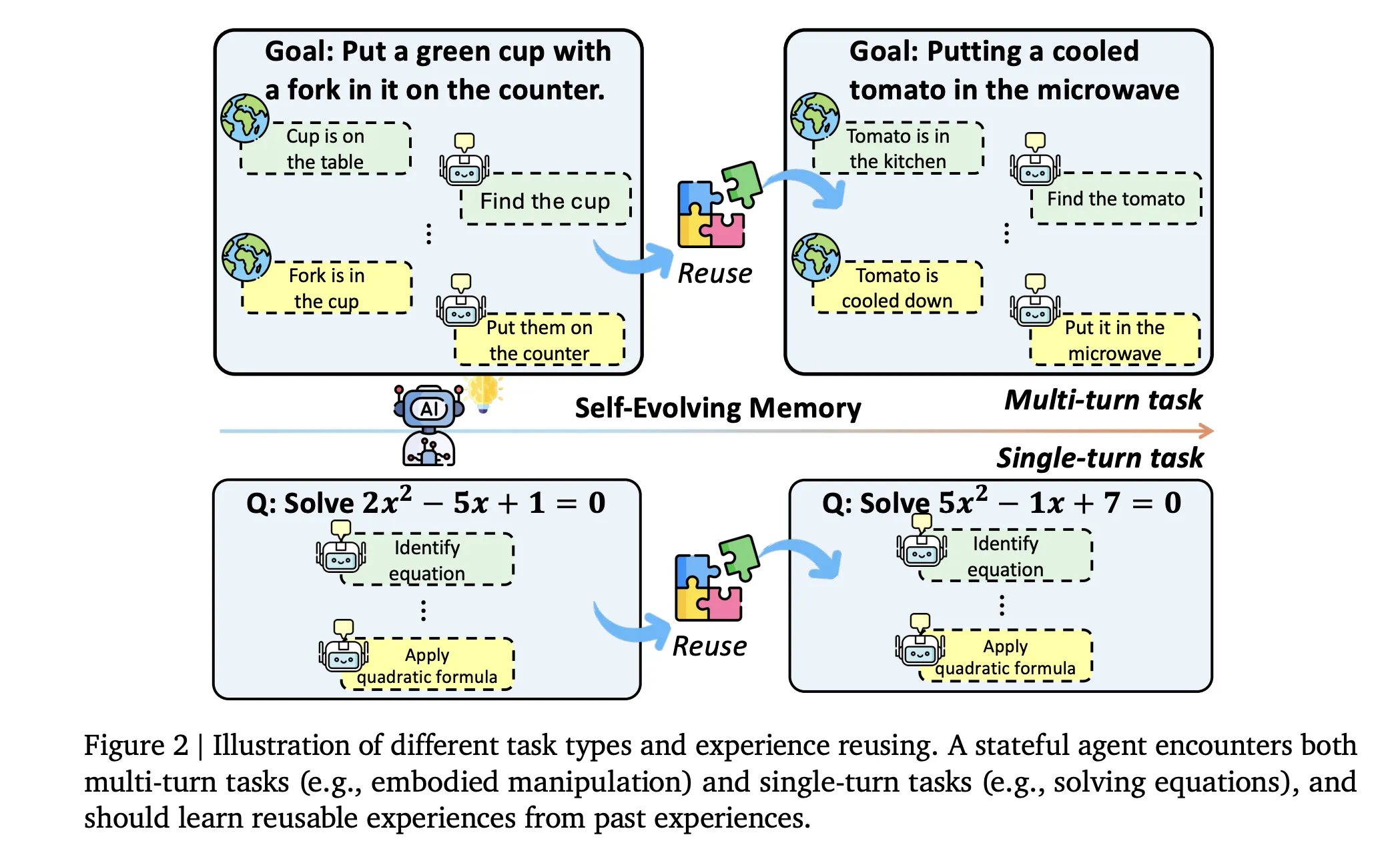
Benchmark Design and Work Stream
Research team formalizes a memory-enhanced agent tuple ((f, u, r, c))The base model (F) produces the output, The retrieval module (R) searches a memory store, The context constructor (C) synthesizes a working prompt from the current input and retrieved items, The update function (U) writes new experience entries and develops memory after each step,
Evo-Memory restructures traditional benchmarks sequential work streamsEach dataset becomes an ordered sequence of tasks, where early items lead to strategies that are useful for later ones, suite covers target 24, target 25, GPQA Diamond, MMLU-Pro Economics, Engineering, PhilosophyAnd toolbench For tool use, with multi-turn environments agentboard Involved alphaworld, babyai, scienceworld, JerichoAnd PDDL Plan.
evaluation is done simultaneously four axisSingle turn tasks use exact matching or answer accuracy, The embedded environment reports success rates and progress rates, Step efficiency measures the average steps taken per successful task, Sequence robustness tests whether performance is stable when the task sequence changes,

XPRAG, a minimal experience reuse baseline
To determine the lower bound, the research team defines xpragEvery interaction becomes a structured experience lesson with template ⟨xI,yI,,fI⟩where xI The input is, yI,The model output and F isI There is feedback, for example an accuracy signal. At a new step
The XPRAG agent does not change the control loop. This is still a single shot call to Backbone, but now augmented with explicitly stored prior functions. The design is deliberately simple so that any benefits can be attributed to evo-memory Work Level Experience RecoveryNot for new scheme or device abstraction.
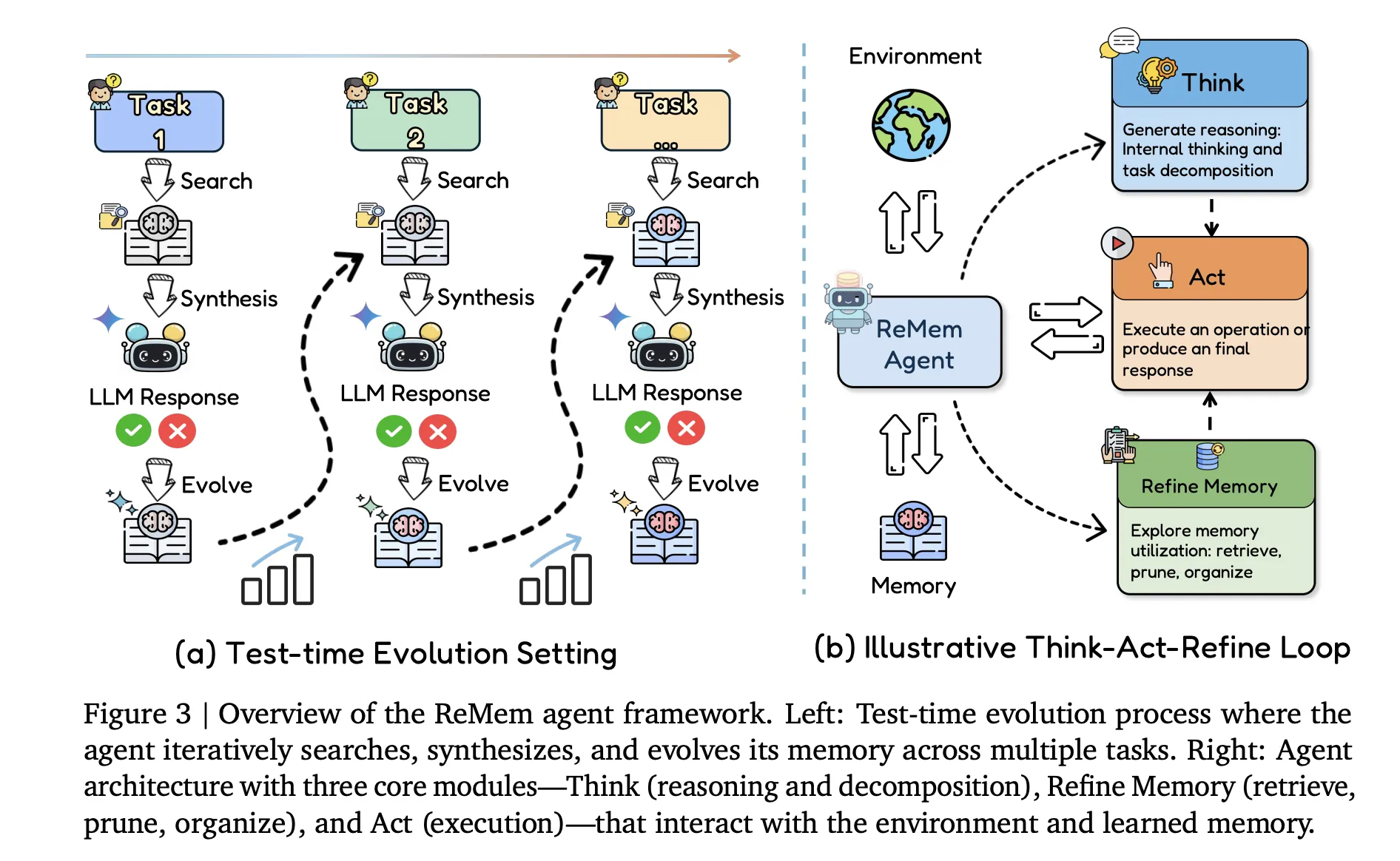
ReMEM, Action Think Memory Refine
The main contribution of the agent side is rememberOne refine action-thinking-memory Pipelines are built on top of the same Backbone model. At each internal step, given the current input, memory state, and traces of previous logic, the agent chooses one of Three operations:
- Thinking Intermediate logic generates traces that decompose the function.
- Work Emits an environment action or final response visible to the user.
- refined Experience performs meta reasoning on memory by retrieving, sorting, and rearranging entries.
This loop induces a Markov decision process where the state includes the query, current memory, and ongoing thoughts. Within a phase the agent can interleave multiple Think and Refine operations, and the phase ends when an Act operation is issued. Unlike standard React style agents, memory is no longer a fixed buffer. It becomes an explicit object about which the agent reasons and edits during inference.

Logic, tools and results on embedded environments
The research team quickly implemented all the methods gemini 2.5 flash And cloud 3.7 sonet under an integrated discovery-prediction-development Etiquette. This isolates the effect of memory architecture, as cueing, search, and feedback are kept constant at the baseline.
On the single turn benchmark, the developed memory methods produce consistent but moderate gains. For Gemini 2.5 flash, ReMEM reaches average precision matching 0.65 in AIME 24, AIME 25, GPQA Diamond and MMLU Pro subsets, and 0.85 and 0.71 API and accuracy on toolbench. XPRAG also performs strongly with average 0.60And the agent outperforms many complex designs, such as workflow memory and dynamic cheatsheet variants.
The impact is larger in a multi-turn environment. On Cloud 3.7 Sonnet, REMEM reaches success and progress 0.92 and 0.96 on alphaworld, 0.73 and 0.83 On BabyAI, 0.83 and 0.95 More on PDDL 0.62 and 0.89 On Scienceworld, giving average 0.78 success And 0.91 progress In the dataset. On Gemini 2.5 flash, ReMEM achieves average 0.50 success And 0.64 progressImprovements to history and React style baselines across all four environments.
Stage efficiency is also improved. In Alphaworld, the average steps to complete a task are reduced 22.6 For the baseline of history 11.5 For rimem. Lightweight designs like Xpressant and Xpreg also reduce steps, which indicates that even simple task level experience reuse can make behavior more efficient without architectural changes to the backbone.
Another analysis is related to benefits work equality within each dataset. Using the embeddings from the retriever encoder, the research team calculates the average distance from tasks to their cluster center. The margin of rem at the history baseline is strongly correlated with this similarity measure, as described by the Pearson correlation. 0.72 On Gemini 2.5 Flash and 0.56 On cloud 3.7 sonnet. Structured domains like PDDL and Alphaworld show large improvements compared to diverse sets like AIME25 or GPQA Diamond.
key takeaways
- Evo-Memory is a comprehensive streaming benchmark that transforms standard datasets into ordered tasks, so that agents can retrieve, integrate, and update memories over time instead of relying on static conversation recall.
- The framework formalizes memory augmented agents as tuples ((F, U, R, C)) and implements more than 10 representative memory modules, including retrieval based, workflow and hierarchical memories, which are evaluated on 10 single turn and multi turn datasets in reasoning, question answering, tool usage and embodied environments.
- XPRAG provides a minimal experience reuse baseline that stores each task interaction as a structured text record with inputs, models outputs, and feedback, then derives the same experiences as reference instances for new tasks, already continuously improving on a purely history-based baseline.
- ReMem extends the standard React style loop with an explicit Think, Act, Refine memory control cycle that lets the agent actively retrieve, prune, and reorganize its memory during inference, leading to higher accuracy, higher success rates, and fewer steps on both single turn reasoning and long horizon interactive environments.
- Across the Gemini 2.5 Flash and Cloud 3.7 Sonnet backbone, self-evolving memories like XPRAG and especially ReMEM treat small models like robust agents at test time, improving accurate matching, success and progress metrics without any retraining of base model weights.


Editorial Notes
Evo memory is a useful step to evaluate self-evolved memory in LLM agents. This forces models to work on sequential work streams rather than discrete signals. It compares more than 10 memory architectures under a single framework. Simple methods like XPRAG already show clear benefits. REMEM’s action, think, and refinement of the memory loop improves matching precision, success, and progress without retraining the base weights. Overall, this research work makes test time evolution a solid design goal for LLM agent systems.
check it out paperFeel free to check us out GitHub page for tutorials, code, and notebooksAlso, feel free to follow us Twitter And don’t forget to join us 100k+ ml subreddit and subscribe our newsletterwait! Are you on Telegram? Now you can also connect with us on Telegram.

Michael Sutter is a data science professional and holds a Master of Science in Data Science from the University of Padova. With a solid foundation in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data engineering, Michael excels in transforming complex datasets into actionable insights.

