DeepSeek researchers are attempting to solve a precise problem in training large language models. Residual connections made very deep networks trainable, hyperconnections widened that residual stream, and training then became unsustainable at scale. The new method MHC, Manifold Constrained Hyperconnections, maintains the rich topology of hyperconnections but locks the mixing behavior to a well-defined manifold so that signals remain numerically stable very deep in the stack.
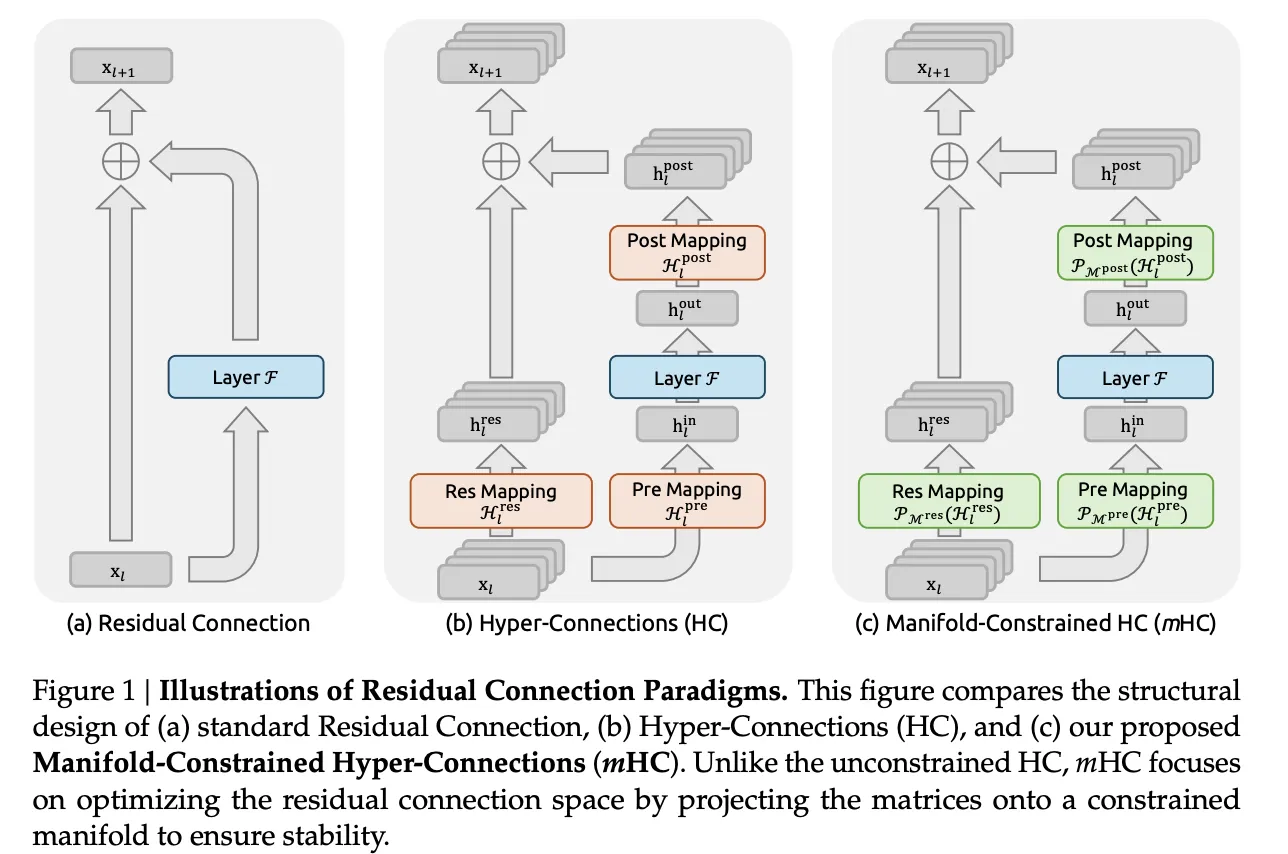
From Residual Connection to Hyper Connection
Standard residual connections, such as in Resnets and transformers, propagate activation alongL+1=xI+f(xI,wI,
The detection path preserves magnitude and keeps the gradient usable even when you stack multiple layers.
Hyperconnections generalize this structure. Instead of a single residual vector of size C, the model maintains an n stream buffer 𝑥𝑙∈𝑅𝑛×𝐶Three learned mappings control how each layer reads and writes to this buffer:
- hlEast The layer selects a mixture of streams as input.
- F is the general attention or feed forward sublayer
- hlPost Writes the result back to n stream buffers
- hlrace∈Rn×n mixes streams between layers
The form of update is
xL+1=HlracexI+HlPostf(hlEastxI,wl)
With n set to 4, this design increases expressivity without a large increase in floating point cost, which is why hyper connections improve downstream performance in language models.
Why do Hyper connections become unstable?
The problem appears when you look at the residual mixer product in multiple layers. In experts’ 27B mixture model, DeepSeek studies composite mapping
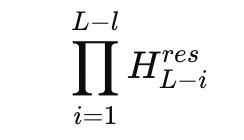
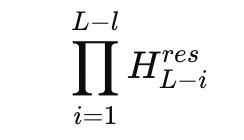
And defines the Amax gain magnitude based on the maximum row and column sum. This metric measures the worst-case amplification in the forward and reverse signal paths. In the hyperconnection model, this gain peaks around 3000, which is far from the ideal value of 1 that you would expect from a stable residual path.
This means that small deviations per layer turn into very large amplification factors in depth. Training logs show loss spikes and unstable gradient parameters relative to the baseline residual model. Also, having multiple stream buffers increases the memory traffic for each token, which makes naive scaling of Hyper Connections unattractive for producing large language models.
Manifold Constrained Hyper Connection
MHC Multi Stream keeps the residual idea but blocks out the dangerous part. residual mixture matrix Hlr e Now the whole n by n no longer occupies space. Instead, it is projected onto a manifold of doubled stochastic matrices, also called Birkhoff polytopes. All entries in that set are non-negative and the sum of each row and each column is 1.
The DeepSeek team enforces this constraint with the classical Sinkhorn Knop algorithm from 1967, which alternates row and column normalization to approximate a doubly stochastic matrix. The research team uses 20 iterations per layer during training, which is enough to keep the mapping close to the target while keeping the cost manageable.
Under these constraints, Hlr exl Behaves like a convex combination of residual currents. The total feature mass is preserved and the parameters are tightly regularized, eliminating the explosive growth seen in plain hyperconnections. The research team also standardizes the input and output mappings so that the coefficients are non-negative, which avoids cancellation between streams and keeps interpretation as clear as averaging.
The composite Amax gain magnitude with MHC remains limited and reaches about 1.6 in the 27B model, while peaking near 3000 for the unrestricted version. This is a reduction of about 3 orders of magnitude in worst-case amplification, and this comes from a direct mathematical constraint rather than from tuned tricks.
System work and training overhead
Limiting each residual mixer with sinkhorn style iterations increases cost on paper. The research team addresses this with several system options:
- Fused kernels combine rmsnorm, estimation, and gating for MHC mapping to keep memory traffic low.
- Recalculation based activation checkpointing trades for memory by recalculating MHC activations during backprop for a block of layers.
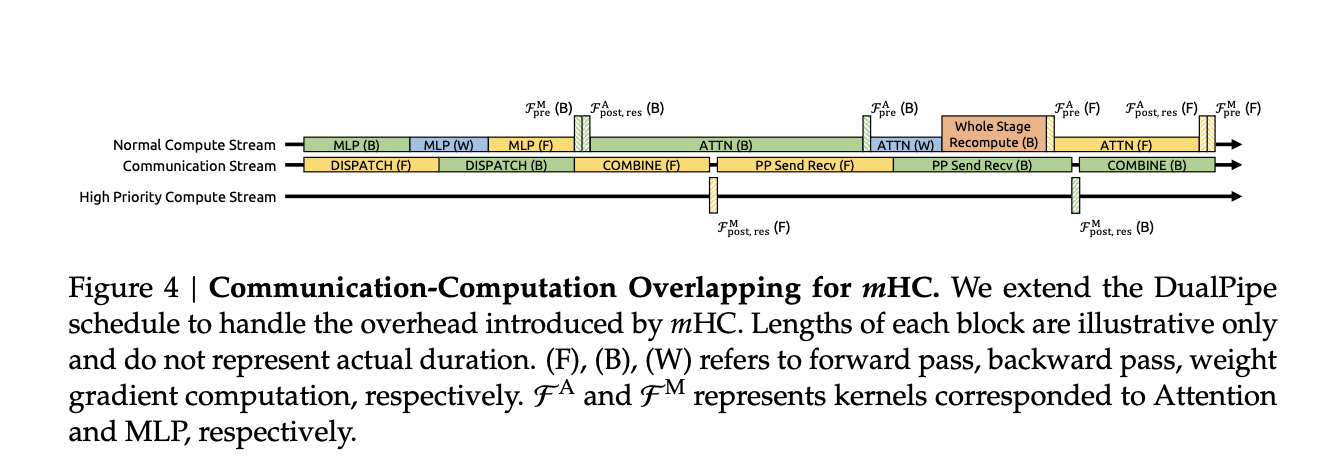
- Integration with pipeline schedules like DualPipe overlaps communication and recalculation, so additional tasks don’t disrupt the training pipeline
In large-scale in-house training, MHC with expansion rate N equal to 4 adds approximately 6.7 percent training time overhead relative to the baseline architecture. That figure already includes both additional computation and infrastructure optimizations from the sinkhorn noop.

Empirical results
The research team trains a mixture of 3B, 9B and 27B expert models and evaluates them on a standard language model benchmark suite, including tasks such as BBH, DROP, GSM8K, Hellasvag, MMLU, PIQA and TRIVIAQA.
For the 27B model, the numbers reported on a subset of tasks clearly show the pattern:
- Baseline: BBH 43.8, Drop F1 47.0
- With Hyper Connection: BBH 48.9, Drop 51.6
- With MHC: BBH 51.0, Drop 53.9
Hyper connections therefore already provide benefits over the original residual design, and manifold constrained hyper connections further advance performance while restoring stability. Similar trends are seen across other benchmarks and model sizes, and the scaling curves show that the gains persist through the compute budget and full training trajectory, rather than simply convergence.
key takeaways
- MHC stabilizes extended residual currents: MHC, Manifold Constrained Hyper Connections, widens the residual path to 4 interacting streams like HC, but constrains the residual mixing matrices on manifold stochastic matrices, so long distance propagation remains standard controlled rather than explosive.
- Burst gain reduced from ≈3000 to ≈1.6:27B For the MOE model, the Amax gain magnitude of the overall residual mapping approaches 3000 for unrestricted HC, while MHC limits this metric to around 1.6, removing the explosive residual stream behavior that previously broke training.
- Sinkhorn Knopf applies doubly stochastic residual mixing: Each residual mixture matrix is interpolated with approximately 20 Sinkhorn Knop iterations so that both rows and columns sum to 1, leading to a convex combination of mapping permutations, which restores behavior-like identity while allowing rich cross stream communication.
- Small training overhead, measurable downstream benefits: In the 3B, 9B and 27B DeepSeq MOE models, MHC improves benchmark accuracy, for example by about 2.1 percent over BBH for the 27B model, while adding only 6.7 percent training time overhead through the fused kernel, recompute, and pipeline aware scheduling.
- Introduces a new scaling axis for LLM design: Instead of simply scaling parameters or reference length, MHC shows that explicitly designing the topology of the residual stream and manifold constraints, for example residual width and structure, is a practical way to unlock better performance and stability in future large language models.
check it out full paper here, Also, feel free to follow us Twitter And don’t forget to join us 100k+ ml subreddit and subscribe our newsletterwait! Are you on Telegram? Now you can also connect with us on Telegram.
Asif Razzaq Marktechpost Media Inc. Is the CEO of. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the potential of Artificial Intelligence for social good. Their most recent endeavor is the launch of MarketTechPost, an Artificial Intelligence media platform, known for its in-depth coverage of Machine Learning and Deep Learning news that is technically robust and easily understood by a wide audience. The platform boasts of over 2 million monthly views, which shows its popularity among the audience.