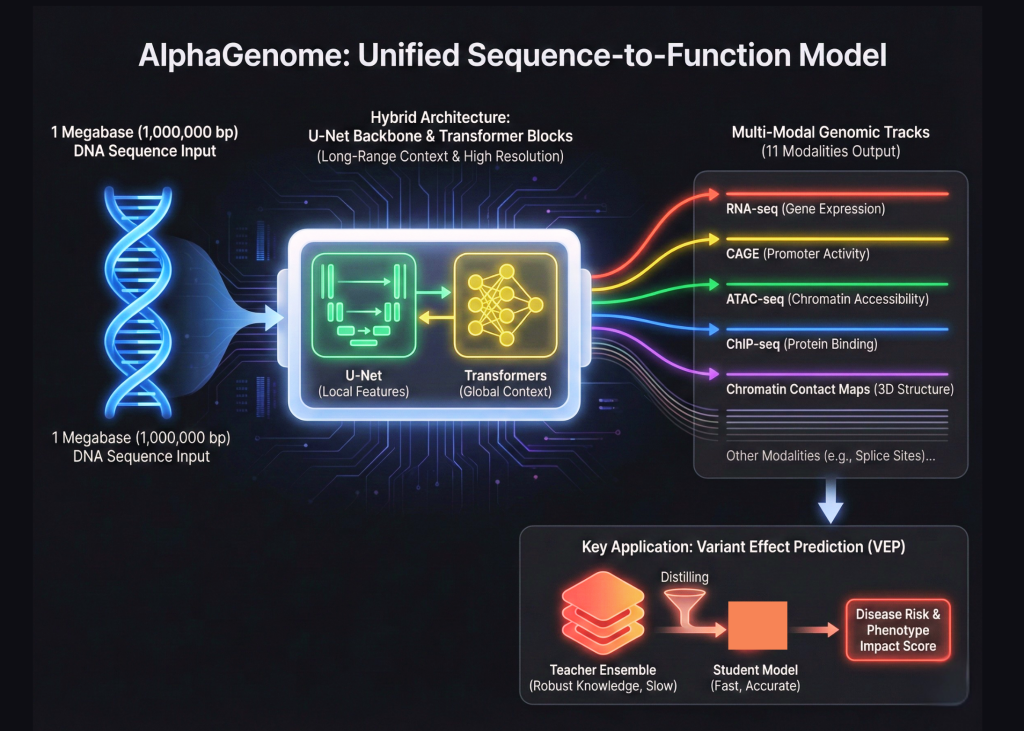
Google DeepMind is expanding its biological toolkit beyond the world of protein folding. Following the success of AlphaFold, Google’s research team has introduced AlphaGenome. It is an integrated deep learning model designed for sequencing genomics tasks. This represents a major change in how we model the human genome. AlphaGenome does not treat DNA as simple text. Instead, it processes a 1,000,000 base pair window of raw DNA to predict the functional state of a cell.
Bridging the scale gap with hybrid architecture
The complexity of the human genome comes from its scale. Most existing models struggle to see the big picture while keeping an eye on the finer details. AlphaGenome solves this by using a hybrid architecture. It connects the U-Net backbone with the transformer blocks. This allows the model to capture long-range interactions across 1 megabase of sequence while maintaining base pair resolution. It’s like creating a system that can read a thousand page book and still remember the exact location of a comma.
Mapping of sequences to functional biological modalities
Alphagenome is a sequence of function model. This means that its primary goal is to map DNA sequences directly to biological activities. These activities are measured in genomic tracks. The research team trained AlphaGenome to predict 11 different genomic modalities. These modalities include RNA-seq, CAGE, and ATAC-seq. They also include ChIP-seq for various transcription factors and chromatin contact maps. By predicting all of these tracks together, the model gains a holistic understanding of how DNA regulates the cell.
The power of multi-task learning in genomics
AlphaGenome’s technological advancement lies in its ability to handle 11 different types of data simultaneously. In the past, researchers often created separate models for each task. AlphaGenome uses a multi-task learning approach. This helps the model learn shared features across different biological processes. If the model understands how the protein binds to the DNA, it can better predict how the DNA will be expressed as RNA. This integrated approach reduces the need for multiple distinct models.
Advancing differential impact prediction through distillation
One of the most important applications for alphagenomes is variant effect prediction or VEP. This process determines how a single mutation in DNA affects the body. Mutations can lead to diseases such as cancer or heart disease. AlphaGenome Teachers excel at this by using a specific training method called student distillation. The research team first created a set of ‘all fold’ teacher models. These teachers were trained on vast amounts of genomic data. Then, they distilled that knowledge into a single student model.
Synthesis of knowledge for precision medicine
This distillation process makes the model faster and more robust. This is a standard way of compressing knowledge. However, applying it to genomics at this scale is a new milestone. The student model learns to replicate the high-quality predictions of the teacher group. This allows it to identify harmful mutations with high accuracy. The model can also predict how mutations in a distant regulatory element might affect distant genes on the DNA strand.
High-performance computing with JAX and TPU
The architecture is implemented using JAX. JAX is a high performance numerical computing library. It is often used for high-level machine learning at Google. Using JAX allows AlphaGenome to run efficiently on a Tensor Processing Unit or TPU. The research team used sequence similarity to handle the huge 1 megabase input window. This ensures that memory requirements do not explode as the sequence length increases. This shows the importance of selecting the right framework for large-scale biological data.
Transfer learning for data-scarce cell types
AlphaGenome also addresses the challenge of lack of data in some cell types. Because it is a foundation model, it can be fine-tuned for specific tasks. The model learns common biological rules from large public datasets. These rules can then be applied to rare diseases or specific tissues where data are difficult to find. This transfer learning ability is one of the reasons why the alphagenome is so versatile. It can predict how a gene will behave in a brain cell, even if it is trained primarily on liver cell data.
Toward a new era of personalized care
In the future, the alphagenome may usher in a new era of personalized medicine. Doctors can use the model to scan a patient’s entire genome down to 1,000,000 base pair fragments. They can accurately identify which variants are likely to cause health problems. This would allow treatments that are tailored to an individual’s specific genetic code. AlphaGenomes move us closer to this reality by providing a clear and accurate map of the functional genome.
Setting the standards for biological AI
AlphaGenome also represents a turning point for AI in genomics. This proves that we can model the most complex biological systems using the same principles used in modern AI. By combining U-Net structures with Transformers and using teacher-student distillation, the Google DeepMind team has set a new standard.
key takeaways
- Hybrid Sequence Architecture: AlphaGenome uses a special hybrid design that combines a u-net with spinal cord Transformer Block. This allows the model to process huge windows 1,000,000 base pairs While maintaining the high resolution required to identify single mutations.
- Multi-Modal Functional Prediction: The model is trained to predict 11 different genomic modalities Together, that includes RNA-seq, CAGE, and ATAC-seq. By learning these different biological tracks together, the system gains a holistic understanding of how DNA regulates cellular activity in different tissues.
- Teacher-Student Distillation: To achieve industry leading accuracy Variant Effect Prediction (VEP)The researchers used the distillation method. They transferred knowledge from a set of high-performing ‘teacher’ models to a single, efficient ‘student’ model that is faster and more robust at identifying disease-causing mutations.
- Built for high performance computing: The framework is implemented in Jax and optimized for tpu. By using sequence similarity, AlphaGenome can handle the computational load of analyzing megabase scale DNA sequences without exceeding memory limits, making it a powerful tool for large-scale research.
check it out paper And repo. Also, feel free to follow us Twitter And don’t forget to join us 100k+ ml subreddit and subscribe our newsletter. wait! Are you on Telegram? Now you can also connect with us on Telegram.