Los Angeles, December 11, 2025 – MarkTechPost has released the ML Global Impact Report 2025 (AIResearchTrends.comThe analysis for this academic report includes more than 5,000 articles from more than 125 countries, published within the Nature family of journals between January 1 and September 30, 2025. The scope of this report is strictly limited to this specific work and is not a comprehensive assessment of global research. This report focuses solely on the specific work presented and does not represent a complete assessment of worldwide research.
ML Global Impact Report 2025 Focuses on three main questions:
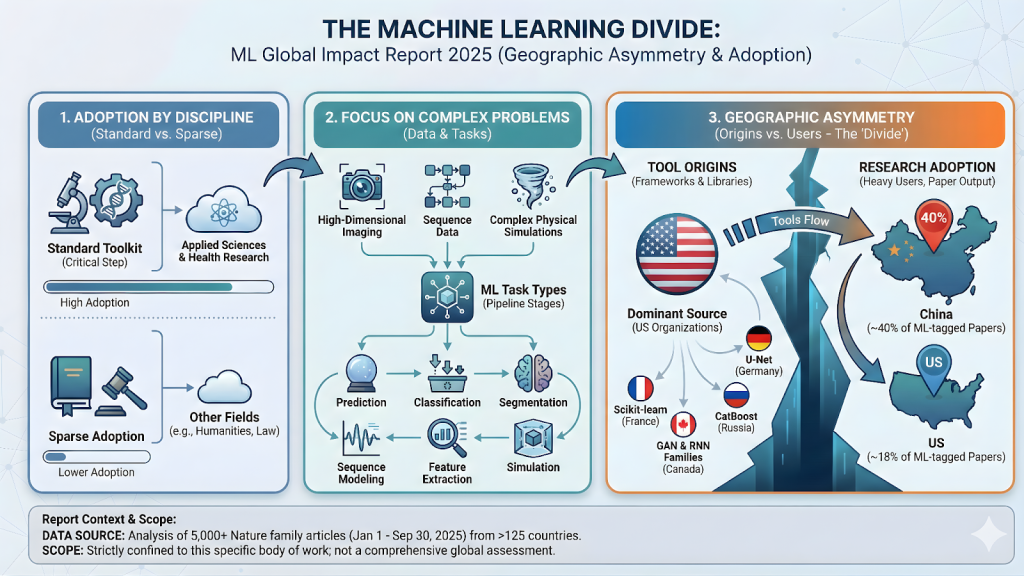
- In which disciplines ML has become part of the standard methodology toolkit, and where its adoption is still low.
- What types of problems are most likely to rely on ML, such as high-dimensional imaging, sequence data, or complex physical simulations.
- Based on the global footprint of these selected 5,000 papers, how ML usage patterns vary by geography and research ecosystem.
ML has often become part of the standard methodology toolkit within the disciplines of applied science and health research, where it is often employed as a key step within a larger experimental workflow rather than being the main subject of research. Analysis of the papers indicates that ML adoption is concentrated in these domains, with tools available to enhance existing research pipelines. The report aims to distinguish these areas of common use from other areas where integration of machine learning is less common.
The types of problems that rely on machine learning include complex data analysis tasks, such as high-dimensional imaging, sequence data analysis, and complex physical simulations. To understand where ML is being applied, the report tracks specific task types, including prediction, classification, segmentation, sequence modeling, feature extraction, and simulation. This classification highlights the usefulness of machine learning at various stages of the research process, from initial data processing to final output generation.
ML usage patterns show a distinct geographic separation between the origins of the tool and heavy users of the technology. Most of the machine learning tools cited in the corpus originate from organizations based in the United States, which maintain many widely used frameworks and libraries. In contrast, China is identified as the largest contributor of research papers, contributing about 40% of all ML-tagged papers, which is significantly higher than the United States’ contribution of about 18%. The report also highlights the global ecosystem by citing tools originating from Canada, including the GAN and RNN families, as well as frequently used non-US tools such as Scikit-Learn (France), U-Net (Germany), and CatBoost (Russia). overall, ML Global Impact Report 2025 Provides deep insight into the global research ecosystem, highlighting how machine learning has become a standard methodological tool primarily within applied science and health research. The analysis reveals a concentration of ML use on complex data challenges such as high-dimensional imaging and physical simulation. A key finding is the clear geographical divide between the origins of ML tools – many of which are maintained by US organizations – and among the heaviest users of the technology, with China accounting for a significantly higher number of ML-tagged research papers in the analyzed corpus. These patterns are specific Over 5,000 Nature Family articles were analysed, underscoring the report’s focused approach to current research workflows.

Michael Sutter is a data science professional and holds a Master of Science in Data Science from the University of Padova. With a solid foundation in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data engineering, Michael excels in transforming complex datasets into actionable insights.

