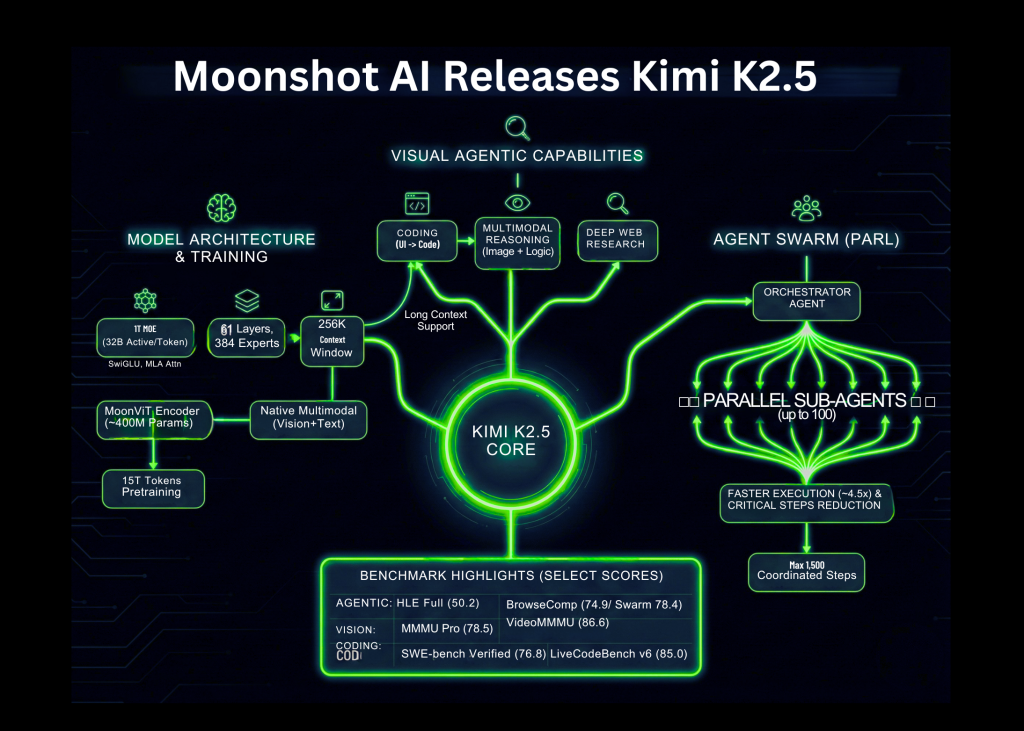
Moonshot AI has released Kimi K2.5 as an open source visual agentic intelligence model. It combines a great mix of an expert language backbone, a native vision encoder, and a parallel multi-agent system called Agent Swarm. The model targets coding, multimodal reasoning, and deep web research, with strong benchmark results on agentive, vision, and coding suites.
Model Architecture and Training
KM K2.5 is experts’ mixing model with 1T total parameters and approximately 32B active parameters per token. The network has 61 layers. It uses 384 experts, with 8 experts elected per token as well as 1 shared expert. The attention hidden size is 7168 and there are 64 attention vertices.
The model uses MLA attention and Swiglu activation function. The size of the tokenizer vocabulary is 160K. The maximum context length during training and inference is 256K tokens. It supports long tool traces, long documents, and multi-step research workflows.
The vision is controlled by a MoonVIT encoder with approximately 400M parameters. Visual tokens are trained with text tokens in a single multimodal backbone. Kmi K2.5 is achieved by continuous pre-training on approximately 15T tokens of mixed vision and text data on top of the Kmi K2 base. This basic multimodal training is important because the model learns joint structures on images, documents, and language from the beginning.
Checkpoint Transformers released with version 4.57.1 or newer support standard inference stacks such as VLLM, SGLang, and KTransformers. Quantized INT4 variants are available, reusing the method of KM K2 thinking. This allows deployment on commodity GPUs with low memory budgets.
Coding and multimodal capabilities
KM K2.5 is positioned as a robust open source coding model, especially when code generation relies on visual context. The model can read UI mockups, design screenshots, or even videos, then emit structured frontend code with layout, styling, and interaction logic.
Moonshot shows examples where the model reads a puzzle image, reasons about the shortest path, and then writes code that produces a visualized solution. It exhibits cross modal reasoning, where the model combines image understanding, algorithm planning, and code synthesis in a single flow.
Because K2.5 has a 256K reference window, it can keep long specification histories in reference. A practical workflow for developers is to combine design assets, product documentation, and existing code into one prompt. The model can then refactor or extend the codebase while keeping the visual constraints aligned with the original design.

Agent Swarm and Parallel Agent Reinforcement Learning
A key feature of Kimi K2.5 is Agent Swarm. It is a multi-agent system trained with Parallel Agent Reinforcement Learning, PARL. In this setup an orchestrator agent decomposes a complex goal into multiple sub-tasks. It then activates domain specific sub-agents to work in parallel.
The KM team reports that K2.5 can manage up to 100 sub-agents within a single task. It supports up to 1,500 coordinated steps or tool calls at a time. This parallelism results in completion approximately 4.5 times faster than a single agent pipeline on comprehensive search tasks.
PARL introduces a metric called Critical Steps. The system rewards policies that minimize the number of sequential steps required to solve the task. This discourages simple sequential planning and prompts the agent to divide the work into parallel branches while maintaining continuity.
An example from KM Team is a research workflow where the system needs to search for multiple specific creators. The orchestrator uses agent swarms to generate a large number of researcher agents. Each agent searches different areas of the web, and the system merges the results into a structured table.

benchmark performance
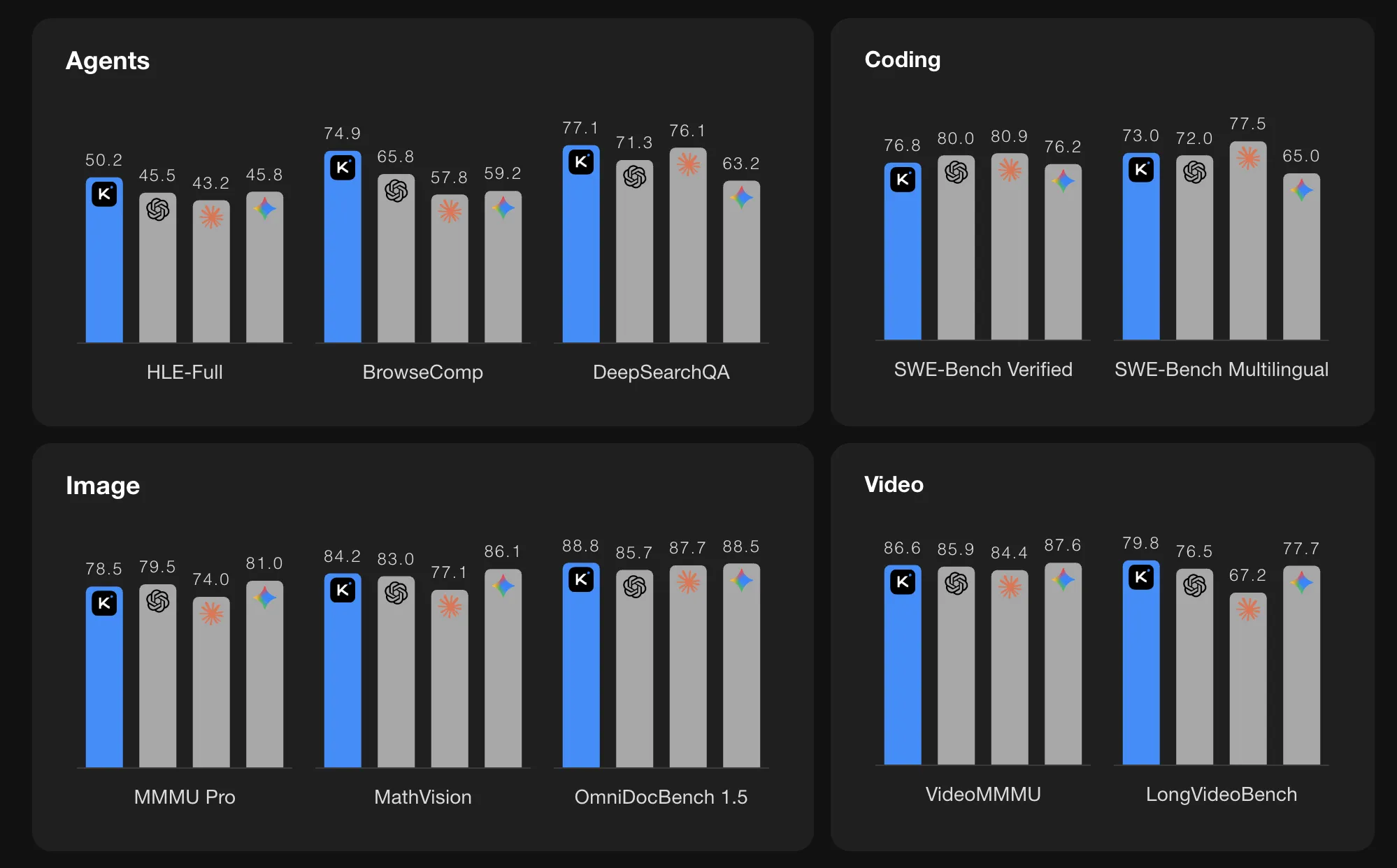
On agentic benchmarks, the Kimi K2.5 reports strong numbers. The score on HLE Full with tools is 50.2. The score on BrowseComp is 74.9 with reference management. In Agent Swarm mode the BrowseComp score increases to 78.4 and WideSearch metrics also improve. The KM team compares these values with GPT 5.2, Cloud 4.5, Gemini 3 Pro, and DeepSeek V3, and K2.5 shows the highest scores among the models listed on these specific agentive suites.
The K2.5 also reports high scores on vision and video benchmarks. The mmmu pro is 78.5 and the video mmmu is 86.6. The model performs well on OmniDocBench, OCRBench, WorldVQA and other document and scene understanding tasks. These results indicate that the MoonVIT encoder and long context training are effective for real-world multimodal problems, such as reading complex documents and reasoning over video.


For coding benchmarks it lists SWE Bench Verified at 76.8, SWE Bench Pro at 50.7, SWE Bench Multilingual at 73.0, Terminal Bench 2.0 at 50.8, and LiveCodeBench v6 at 85.0. These numbers place K2.5 among the strongest open source coding models currently reported on these tasks.
On long reference language benchmarks, K2.5 reaches 61.0 on Longbench V2 and 70.0 on AA LCR under standard evaluation settings. It achieves high scores on AIME 2025, HMMT 2025 February, GPQA Diamond and MMLU Pro when used in Thinking Mode for Reasoning benchmarks.
key takeaways
- A combination of experts on a trillion scale: KM K2.5 uses an architecture of experts mixing with 1T total parameters and approximately 32B active parameters per token, 61 layers, 384 experts and 256K context length, optimized for long multimodel and tool heavy workflows.
- Native Multimodal Training with MoonVIT: The model integrates a MoonVIT vision encoder of approximately 400M parameters and is trained on approximately 15T of mixed vision and text tokens, so images, documents and language are handled in a unified backbone.
- Parallel Agent Swarm with PARL: Agent Swarm, trained with parallel agent reinforcement learning, can coordinate up to 100 subagents and approximately 1,500 tool calls per task, yielding approximately 4.5 times faster execution than a single agent on extensive research tasks.
- Coding, vision, and agents result in strong benchmarks: K2.5 reports 76.8 on SWE Bench Verified, 78.5 on MMMU Pro, 86.6 on VideoMMMU, 50.2 on HLE Full with Tools, and 74.9 on BrowseComp, which matches or exceeds the discontinued models listed on many agentic and multimodal suites.
check it out technical details And model weight. Also, feel free to follow us Twitter And don’t forget to join us 100k+ ml subreddit and subscribe our newsletter. wait! Are you on Telegram? Now you can also connect with us on Telegram.