recursive language model Its purpose is to break down the common tradeoff between reference length, accuracy, and cost in large language models. Instead of forcing a model to read a huge prompt in one pass, RLMs treat the prompt as an external environment and let the model decide how to inspect it with code, then call itself recursively on smaller pieces.

the basics
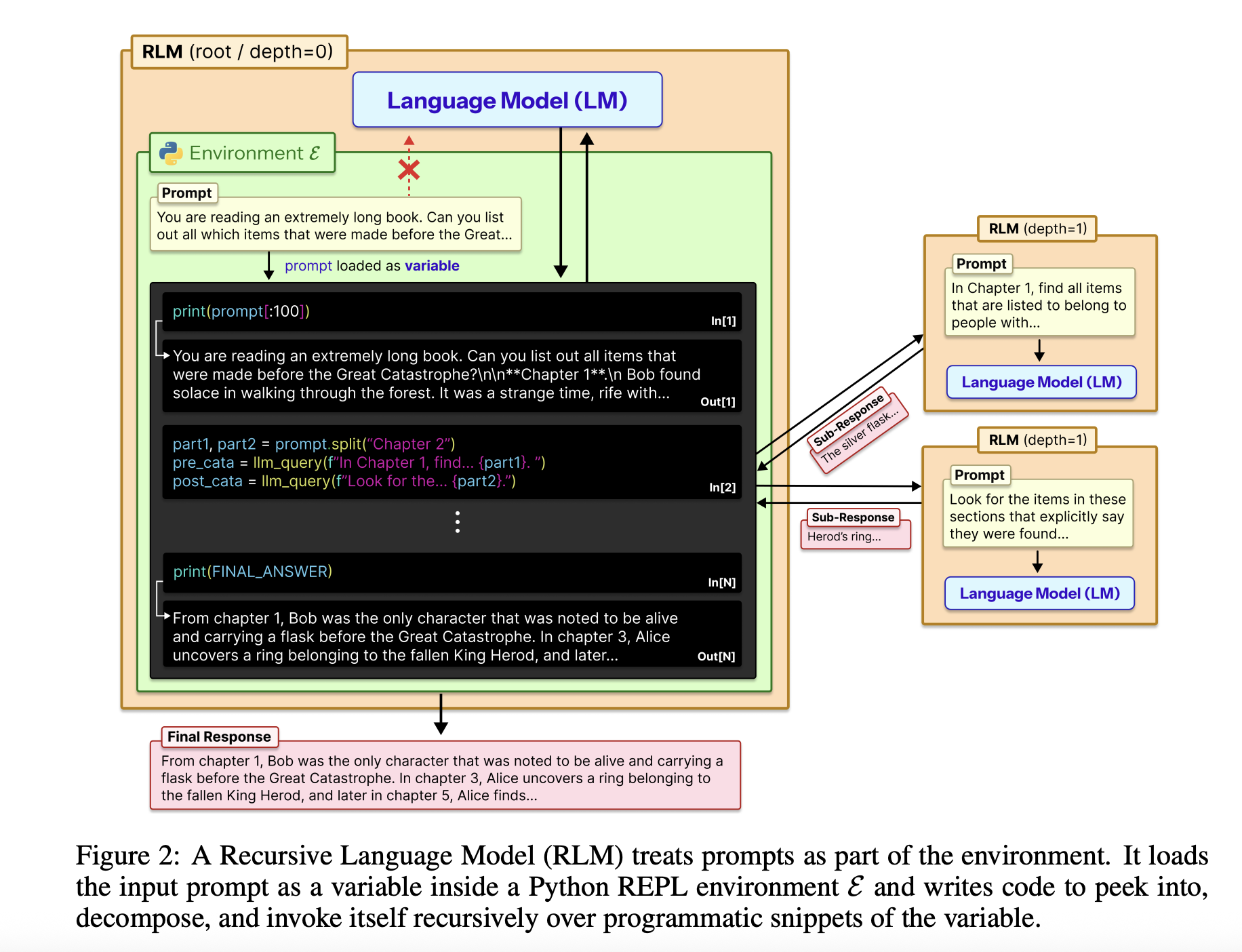
The entire input is loaded into the Python REPL as a single string variable. The root model, for example GPT-5, never sees that string directly in its context. Instead, it receives a system prompt that explains how to read slices of variables, how to write helper functions, generate sub LLM calls, and how to combine the results. The model returns one final text reply, so the external interface remains the same as the standard chat termination endpoint.
The RLM design uses the REPL as a control plane for long context. The environment, typically written in Python, exposes tools such as string slicing, regex searching, and helper functions. llm_query Which calls a smaller model instance, for example GPT-5-mini. The root model writes code that calls these helpers to scan, split, and summarize external context variables. The code can store intermediate results in variables and produce the final answer step by step. This structure makes the prompt size independent of the model context window and turns long context management into a program synthesis problem.

Where does it stand in evaluation?
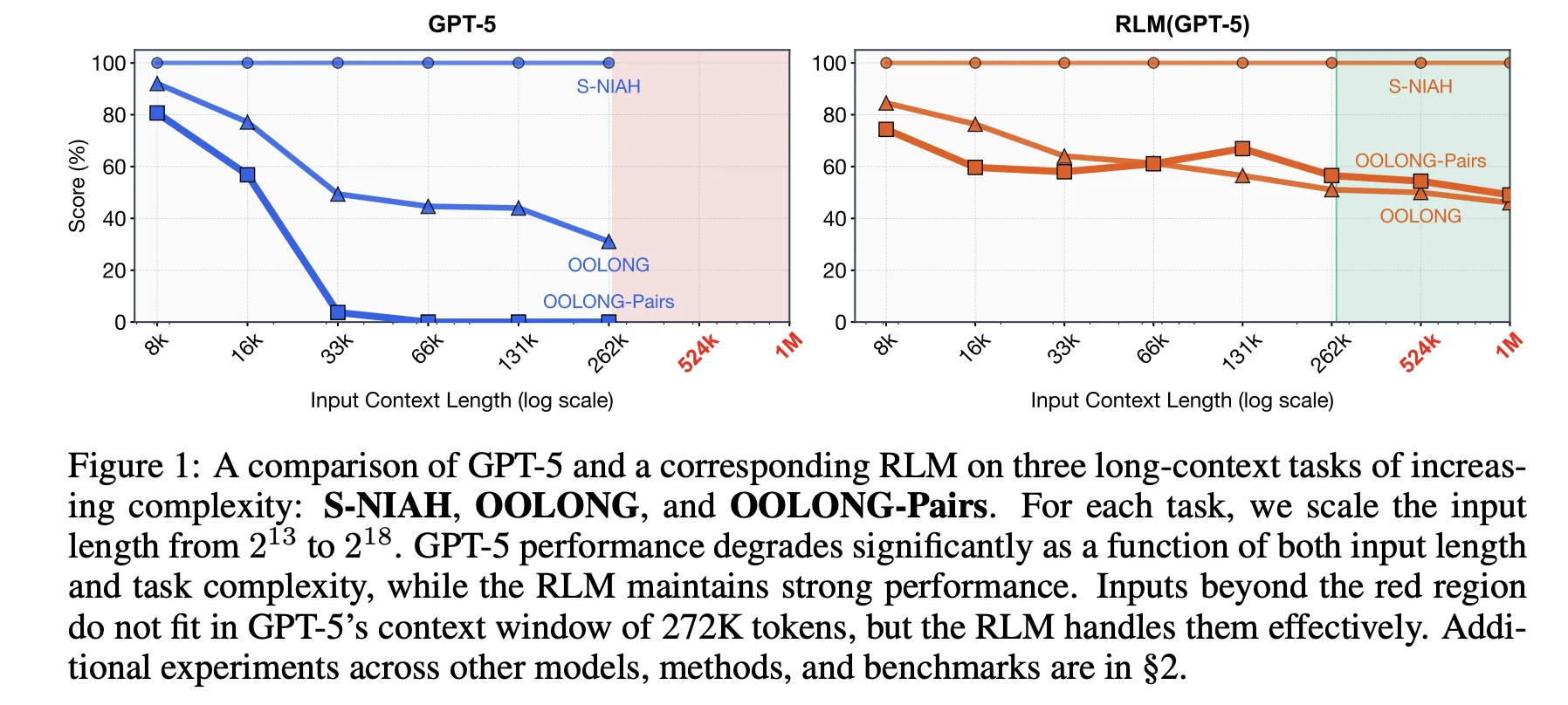
research paper Evaluates this idea on four long reference benchmarks with different computational architecture. The S-NIAH is a needle in the haystack task of increasing complexity. BrowseComp-Plus is a multi hop web style question answering benchmark for up to 1,000 documents. OOLONG is a linear complexity long context reasoning function where the model must transform multiple entries and then aggregate them. OOLONG pairs further increase the difficulty with quadratic pairwise aggregation on inputs. These tasks emphasize both length of context and depth of reasoning, not just retrieval.
On these benchmarks, RLMs give large accuracy gains over direct LLM calls and general long context agents. For GPT-5 on CodeQA, a long document question answer setup, the base model reaches 24.00 accuracy, a summary agent reaches 41.33, while the RLM reaches 62.00 and the RLM without iterations reaches 66.00. For Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B, the score of the base model is 20.00, the score of CodeAct Retrieval Agent is 52.00, and the RLM is 56.00, only the REPL variant has a score of 44.66.
The profit is greatest on the hardest setting, Oolong Pairs. For GPT-5, the direct model is almost useless with F1 equal to 0.04. Summarize and CodeAct agents sit closer to 0.01 and 24.67. The full RLM reaches 58.00 F1 and the non recursive REPL version still gets 43.93. For qen3-coder, the base model remains below 0.10 F1, while the full RLM reaches version 23.11 and the REPL only version 17.34. These numbers show that both REPL and recursive sub calls are important on dense quadratic functions.
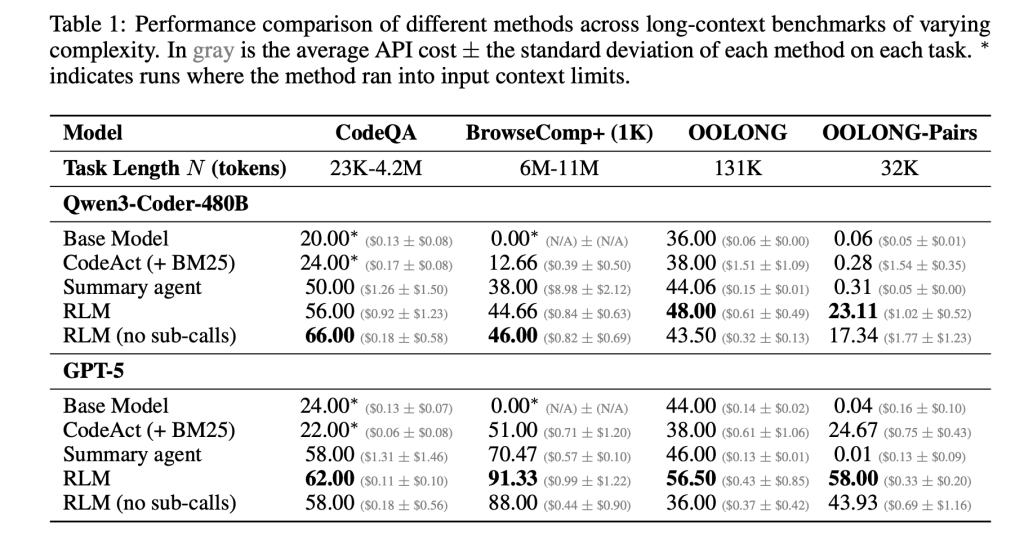

BrowseComp-Plus highlights effective reference expansion. The corpus ranges from approximately 6M to 11M tokens, which is 2 orders of magnitude beyond GPT-5’s 272k token reference window. RLM with GPT 5 maintains strong performance even when given 1,000 documents in the environment variables, while the standard GPT-5 baseline degrades as the document number increases. On this benchmark, RLM GPT5 achieves approximately 91.33 accuracy with an average cost of 0.99 USD per query, while a hypothetical model that reads full references directly would cost between $1.50 and $2.75 at current pricing.
research paper RLM also analyzes the trajectory of the run. Many behavioral patterns emerge. The model often starts with a glance phase where it inspects the first few thousand characters of the context. It then uses grep style filtering with regex or keyword searching to narrow down the relevant rows. For more complex queries, it divides the context into segments and calls LM recursively on each segment to perform labeling or extraction, followed by programmatic aggregation. On long output tasks, RLM stores partial outputs in variables and concatenates them together, which bypasses the output length limitation of the base model.
Prime Intellect’s new approach
Prime Intellect Team This concept has been turned into a concrete environment, RLMEnv, integrated into their validator stack and Environment Hub. In their design, the main RLM contains only the Python REPL, while sub RLMs receive heavy tools like web search or file access. REPL exposes one llm_batch function so that the root model can fan out multiple sub queries in parallel, and answer Variable where the final solution should be written and marked as ready. This token abstracts heavy tool output from the main context and allows the RLM to delegate expensive operations to submodels.
primary intelligence Evaluates this implementation on four environments. DeepDive tests web research with search and open tools and very detailed pages. Math Python exposes the Python REPL for difficult competition-style math problems. Oolong reuses the long reference benchmark inside RLMEnv. Verbatim copy focuses on accurate reproduction of complex strings in content types such as JSON, CSV and mixed code. In these environments, both the GPT-5-mini and INTELLECT-3-MoE models benefit from RLM scaffolding in success rates and robustness to very long contexts, especially when tool output would otherwise impact the model context.
Both the paper’s author team and the Prime Intellect team emphasize that current implementations are not fully optimized. RLM calls are synchronous, recursion depth is limited and very long trajectories lead to heavy tails in the cost distribution. The real opportunity is to combine RLM scaffolding with dedicated reinforcement learning so that models can learn better chunking, recursion, and tool usage policies over time. If this happens, RLMs provide a framework where improvements to the base model and system design are directly translated into more capable long-term agents that can consume 10M plus token environments without context decomposition.
key takeaways
Here are 5 short, technical tips you can add within the article.
- RLM rename long reference as an environment variable: Recursive language models treat the entire prompt as an external string in a Python-style REPL, which the LLM inspects and transforms through code, rather than including all tokens directly in the transformer context.
- Estimate time recursion extends context to more than 10M tokens: RLM lets a root model recursively call sub LLMs on selected snippets of context, enabling efficient processing of signals up to about 2 orders of magnitude compared to the base context window, reaching 10M plus tokens on BrowseComp-Plus style workloads.
- RLMs outperform normal long context scaffolding on tough benchmarks: In S-NIAH, BrowseComp-Plus, Oolong and Oolong pairs, the RLM variants of GPT-5 and Qwen3-Coder improve accuracy and F1 over direct model calls, retrieval agents like CodeAct, and summarization agents, while keeping the cost per query comparable or lower.
- REPL only helps variants already, recursion is important for quadratic functions: An ablation that exposes only the REPL without recursive sub calls still gives a performance boost on some tasks, showing the value of offloading context into the environment, but requires a full RLM to achieve large gains on information dense settings such as Oolong pairs.
- Prime Intellect handles RLM through RLMEnv and INTELLECT 3:Prime Intellect team implements the RLM paradigm as RLMENV, where the root LM controls the sandboxed Python REPL, calls tools through sub LMs and writes the final result.
answerDeepDive, with models such as Variables, and INTELLECT-3, reports consistent gains over Mathematica Python, Oolong, and verbatim copy environments.
check it out paper And technical detailsAlso, feel free to follow us Twitter And don’t forget to join us 100k+ ml subreddit and subscribe our newsletterwait! Are you on Telegram? Now you can also connect with us on Telegram.
Asif Razzaq Marktechpost Media Inc. Is the CEO of. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the potential of Artificial Intelligence for social good. Their most recent endeavor is the launch of MarketTechPost, an Artificial Intelligence media platform, known for its in-depth coverage of Machine Learning and Deep Learning news that is technically robust and easily understood by a wide audience. The platform boasts of over 2 million monthly views, which shows its popularity among the audience.
