Tencent Hunyuan researchers have released HY-MT1.5, a multilingual machine translation family that targets both mobile devices and cloud systems with the same training recipe and metrics. HY-MT1.5 includes 2 translation models, HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B, supports mutual translation in 33 languages with 5 ethnic and dialect variations, and is available on GitHub and Hugging Face under open source.
Model families and deployment targets
HY-MT1.5-7B is the upgraded version of WMT25 Championship System Hunyuan-MT-7B. It is optimized for interpretive translation and mixed language scenarios, and adds native support for vocabulary intervention, contextual translation, and formatted translation.
HY-MT1.5-1.8B is the compact variant. It has less than a third of the parameters of HY-MT1.5-7B but provides comparable translation performance in the reported benchmarks. After quantization, the 1.8B model can run on edge devices and support real-time translation.
Quantized HY-MT1.5-1.8B works on devices with about 1 GB of memory and reaches an average response time of about 0.18 seconds for a Chinese input of about 50 tokens, while surpassing mainstream commercial translation APIs in quality. The HY-MT1.5-7B targets server and high end edge deployments, where latency of around 0.45 seconds is acceptable in exchange for higher quality.
overall training framework
The research team defines HY-MT1.5 as a translation specific language model trained with a multi-stage pipeline.
The pipeline has 5 main components:
- general pre-training: The base model is first pre-trained on large-scale multilingual text with language modeling purpose. This creates a shared representation across all languages.
- MT oriented pre-training: The model is then exposed to parallel corpora and translation-oriented objectives. This step aligns the generation distribution with actual translation tasks rather than open-ended text generation.
- Supervised fine tuning: High quality sentence and document level data are used in parallel to fine-tune models with supervised loss. This step accelerates lexical accuracy, domain coverage, and direction specific behavior, such as ZH to EN vs EN to ZH.
- On policy distillation from 7B to 1.8B:HY-MT1.5-7B is used as teacher for HY-MT1.5-1.8B. The research team collects approximately 1 million monolingual prompts in 33 languages, runs them through teachers and uses reverse Kullback Leibler divergence on student rollouts to match teacher distribution. This produces a 1.8B student that inherits most of the translation behavior of the 7B model at very little cost.
- Reinforcement Learning with Rubrics Based Assessment: In the final step, both models are optimized with group relative policy optimization style algorithms and rubrics based reward models. Human reviewers evaluate translations on multiple axes such as accuracy, flow, idiomaticity, and cultural appropriateness. The reward model distributes those points and guides policy updates.
This pipeline is specialized for machine translation. It differs from chat-oriented LLM training by combining translation-focused supervised data, policy distillation within the translation domain, and RL tune with granular translation rubrics.
Benchmark results against open and commercial systems
HY-MT1.5 is evaluated on minority language benchmarks from Flores 200, WMT25 and Mandarin using XCOMET-XXL and CometKiwi.
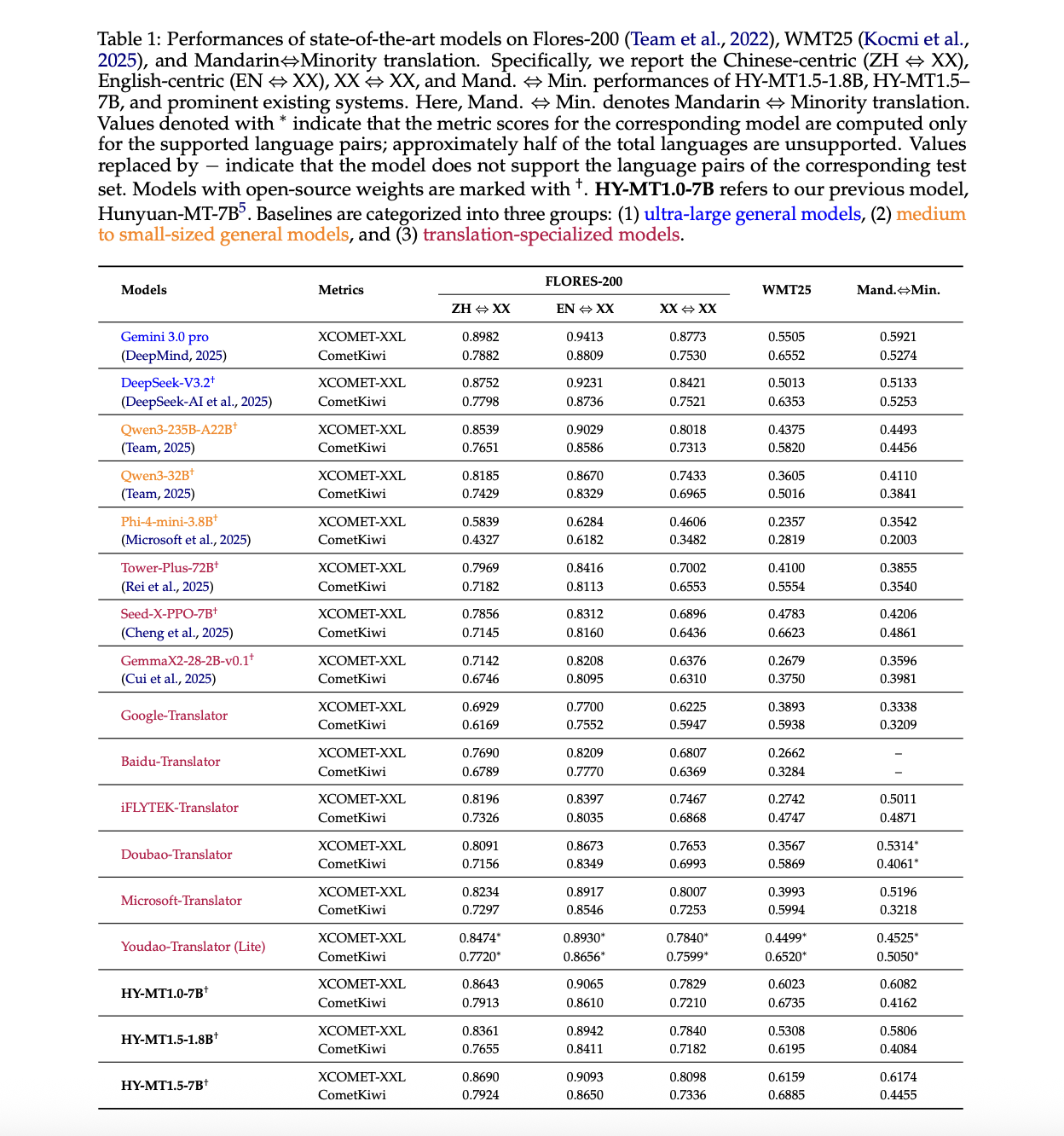
Key results from the above table in the report:
- On the Flores 200, the HY-MT1.5-7B reaches XCOMET-XXL scores of 0.8690 for ZH to XX, 0.9093 for EN to XX, and 0.8098 for XX to XX. It outperforms translation-specific models like the iFLYTEK Translator and Doubao Translator and matches or surpasses mid-sized generic models like the Qwen3-235B-A22B.
- On WMT25, HY-MT1.5-7B XCOMET-XXL reaches 0.6159. This is about 0.065 more than the Gemini 3.0 Pro and well above translation-oriented models like the Seed-X-PPO-7B and Tower-Plus-72B. The score of HY-MT1.5-1.8B is 0.5308, which is still higher than many medium-sized general models and translation systems.
- On minority language pairs from Mandarin, the HY-MT1.5-7B achieves 0.6174 in XCOMET-XXL, which is higher than all baselines including Gemini 3.0 Pro. The 1.8B variant reaches 0.5806 and still surpasses many much larger models such as DeepSeek-V3.2.
In human evaluation on a 0 to 4 scale for Chinese to English and English to Chinese, HY-MT1.5-1.8B achieves an average score of 2.74, which is higher than Baidu, iFLYTEK, Doubao, Microsoft and Google translator systems under the same protocol.
Practical features for product use
The models highlight three quickly driven capabilities that matter in production systems:
- vocabulary intervention: A quick template lets you inject word mappings like “混元珠 → Chaos Pearl”. Without mapping, the model outputs an ambiguous transliteration. With mapping, it enforces a consistent domain specific terminology. This is important for legal, medical or brand restricted content.
- context aware translation: The second template accepts a context block and a sentence for translation. The report suggests that the word “pilot” has been misinterpreted as a person when the context is absent. When a paragraph about a TV series is added, the model correctly translates “pilot” as an episode.
- Preserving translation format: A third template wraps the source
These are implemented as prompt formats, so they are still available when you call public loads through the standard LLM stack.
Quantization and edge deployment
HY-MT1.5-1.8B is evaluated after training using GPTQ with FP8 and Int4 quantization.
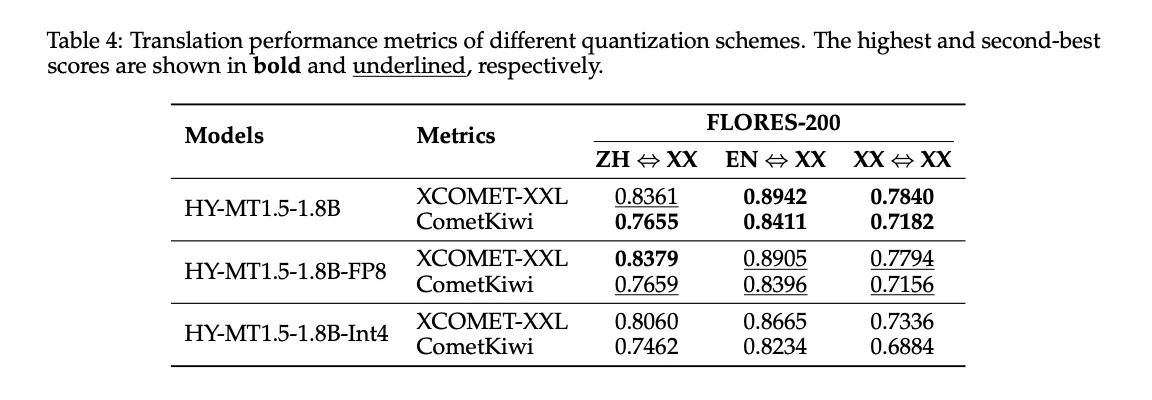

Table 4 above shows:
- FP8 keeps the
- Int4 further reduces the size but brings a clear drop in quality to the Flores 200.
On the hugging face, Tencent publishes both FP8 and GPTQ Int4 variants for the local inference stack, as well as GGUF versions for HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B. Quantization is the mechanism that enables the reported 1 GB memory deployment and low latency on consumer hardware.
key takeaways
- HY-MT1.5 is a 2 model translation family, HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B, which supports mutual translation in 33 languages and 5 dialects or variants, released with open source on GitHub and Hugging Face.
- HY-MT1.5-1.8B is a distillation based edge model that runs on approximately 1 GB of memory with approximately 0.18 second latency for a 50 token Chinese input, while achieving industry leading performance among similarly sized models and surpassing most commercial translation APIs.
- HY-MT1.5-7B is an advanced WMT25 champion system that reaches approximately 95 percent of Gemini 3.0 Pro on Flores 200 and surpasses it on the WMT25 and Mandarin minority benchmarks, competing with much larger open and closed models.
- Both models are trained with a holistic translation specific pipeline that combines general and MT-oriented pre-training, supervised fine-tuning on policy distillation and reinforcement learning guided by rubric-based human assessment, which is critical to their quality and efficiency.
- HY-MT1.5 exposes production-oriented features through signals including terminology interference, context aware translation and format preserved translation, and ships FP8, Int4 and GGUF variants so teams can deploy on devices or servers with standard LLM stacks.
check it out paper, Model weight on HF And GitHub repoAlso, feel free to follow us Twitter And don’t forget to join us 100k+ ml subreddit and subscribe our newsletterwait! Are you on Telegram? Now you can also connect with us on Telegram.

Michael Sutter is a data science professional and holds a Master of Science in Data Science from the University of Padova. With a solid foundation in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data engineering, Michael excels in transforming complex datasets into actionable insights.