AgentCore Gateway now supports API Gateway As organizations explore the potential of agentic applications, they continue to navigate the challenges of using enterprise data as context in large language model (LLM) invocation requests in a manner that is secure and aligned with enterprise policies. To help standardize and secure those interactions, many organizations are using Model Reference Protocol (MCP) specification, which defines how agentive applications can securely connect to data sources and tools.
While MCP has been beneficial for net new use cases, organizations also face challenges with bringing their existing API estate into the agentic era. MCP can certainly wrap existing APIs, but this requires additional work, translating requests from MCP to the RESTful API, ensuring that security is maintained through the entire request flow, and implementing the standard observability required for production deployment.
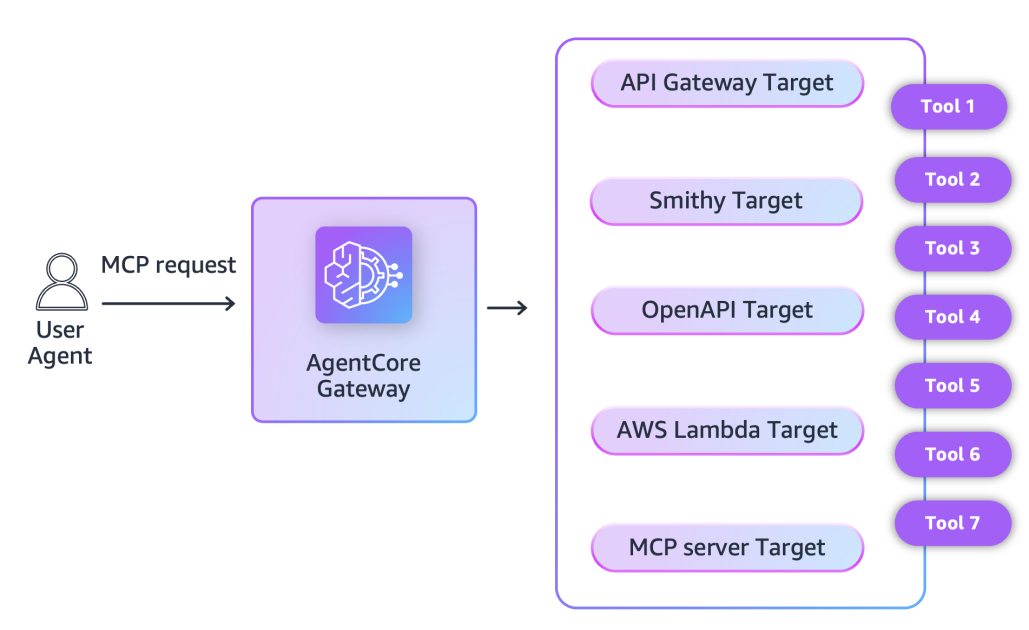
Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Gateway now supports Amazon API Gateway as a target, translating AgentCore Gateway’s MCP requests into API Gateway’s RESTful requests. You can now expose both new and existing API endpoints to agentic applications using MCP with built-in security and observability. This post covers these new capabilities and shows how to implement them.
What’s New: API Gateway support in AgentCore Gateway
AgentCore Gateway now supports existing target types (Lambda functions, openapi schema, blacksmithing model, and mcp Server).
Our customers have successfully built comprehensive API ecosystems using API Gateway, connecting backends across multiple applications. As enterprises move toward next-generation agentic applications, the natural evolution is to expose these existing APIs and backend tools into AI-powered systems, enabling seamless integration between established infrastructure and modern intelligent agents.
This integration between AgentCore Gateway and API Gateway simplifies the connection between API Gateway and AgentCore Gateway. This allows you to target API Gateway directly, so you don’t need to export the API Gateway API as an OpenAPI 3 specification and then add it to AgentCore Gateway as an OpenAPI target.
With this integration, a new API_GATEWAY target type will be added to the AgentCore Gateway, eliminating the manual export/import process. REST API owners can add their API as an AgentCore Gateway target to expose their existing REST APIs as an MCP tool using AgentCore Gateway with few console interactions or a single CLI command. API consumers can connect AI agents to these REST APIs via Model Context Protocol (MCP) and empower their workflows with AI integration. Your agentive applications can now connect to your new or existing API Gateway APIs. This integration between AgentCore Gateway and API Gateway supports IAM and API key authorization.

Both AgentCore Gateway and API Gateway have integration with Amazon CloudWatch Logs, AWS CloudTrail, and AWS X-Ray for observability. Agent developers using this new capability between AgentCore Gateway and API Gateway can use these observability tools.
rehearsal
This post shows you how to set up an existing REST API with API Gateway as the target of AgentCore Gateway. With this integration you can use your existing REST API as a tool for your agentic applications exposed using the AgentCore Gateway.
Prerequisites
For this example, you need the following:
- AWS account with an existing REST API in API Gateway.
- An identity and access management (IAM) role or user that has sufficient permissions to create AgentCore gateways and set up API gateway targets.
You can create a gateway and add a target in several ways:
This post uses Boto3 to set up integration between AgentCore Gateway and API Gateway. For an interactive walkthrough, you can use the Jupyter Notebook sample GitHub,
Set prerequisites for inbound and outbound authorization.
Inbound authorization authenticates incoming user requests. Outbound authorization helps AgentCore Gateway securely connect to gateway targets such as API Gateway on behalf of the authenticated user.

For API Gateway as the target, AgentCore Gateway supports the following types of outbound authorization:
- No authorization (not recommended) – Some target types provide you the option to bypass outbound authorization. We do not recommend this less secure option.
- IAM-based outbound authorization – Use the Gateway Service role to authorize access to a gateway target with AWS Signature version 4 (SIG v4).
- API Key – Use the API key, which is set using the AgentCore Identity, to authorize access to the API Gateway target. API keys created using API Gateway, mapped with API Gateway usage plans, help you monitor and control API usage. Please see this document for more details.
Create an IAM role with the trust policy from the documentation.
- For outbound authorization with IAM-based authorization, the policy must include
execute-api:InvokePermission. Sample Inline Policy:
Once done, update the policy as described in the AgentCore Gateway documentation.
Create an AgentCore Gateway
When using the AgentCore Starter Toolkit, you can create a gateway with the default authorization configuration using Amazon Cognito for JWT-based inbound authorization.
it returns GATEWAY_ID You will need to create a gateway target.
Create an AgentCore Gateway target

Create a target configuration
To create an API Gateway target, you must specify the following as part of the target configuration:
- toolfilter: Use this to determine which resources on the REST API will display as tools on the gateway. Filters also support wildcards in the filterpath.
- tooloverrides (Optional): Use this to allow users to override the tool name and description. You must specify explicit paths and methods.
- restapiid: Use this to pass the API gateway ID.
Below are some examples of target configurations:
Example 1
it exposes receive and post /pets, /pets/get{petId} on gateways and overrides their tool name and description.
Example 2
this will expose get/pet But /pets/get{petId} or anything under /domestic animalsince tooloverrides If not specified, it will use the resource description from the API Gateway.
Credential Provider Configuration
When creating a target, you must also specify the target’s outbound authorization using the credential provider configuration. As discussed above, there are three types of credential providers:
GATEWAY_IAM_ROLE
uses it ROLE_ARN You specified it when you created the gateway. Define the credential provider configuration as follows:
API_KEY
This requires the creation of an API key credential provider with AgentCore Identity.
NO_AUTH
NO_AUTH AgentCore Gateway can be configured by not specifying the credential provider configuration when creating the target. This is not recommended.
Create an AgentCore Gateway target
Now configure your REST API as a gateway target:
Test Gateway with Strands Agent Framework
test gateway with strands agent Framework for listing and calling tools available from the MCP server. You can also use other MCP-compatible agents built with different agentic frameworks.
You will see the following output:
observability
Enable application logging and tracing for your AgentCore Gateway resource. You will see detailed logs to help monitor and troubleshoot your AgentCore Gateway resource. This will include tool calls, request parameters, responses, and errors, if any, made by your agent application.
Example log:
Additionally, the AgentCore Gateway also provides detailed CloudWatch metrics usage metrics (TargetType, IngressAuthType, EgressAuthType, RequestPerception), invocation metrics (invocation, concurrent execution, session), performance metrics (Latency, Duration, TargetExecutionTime), and error rate (Throttles, System Error, User Error).

AgentCore Gateway AWS

To learn more, see the AgentCore Gateway Observability documentation.
cleanliness
To avoid recurring charges, make sure to delete the resources created by running the following code.
conclusion
AgentCore Gateway now supports Amazon API Gateway as a target, exposing REST APIs as MCP-compliant endpoints. You can bring your existing API infrastructure to agentive use cases using your existing security and observability tools.
Visit our developer documentation and workshop To learn more and get started today.
About the authors
 With over 6+ years at AWS, Sparsh Wadhwa The ISV in India brings deep expertise in serverless, event-driven architectures and generative AI to its work with clients. As a solutions architect, he partners with independent software vendors to reimagine their products for the cloud era – from modernizing legacy systems to embedding AI capabilities that differentiate their offerings. Sparsh believes that the best solutions emerge from understanding both the technical possibilities and the business context.
With over 6+ years at AWS, Sparsh Wadhwa The ISV in India brings deep expertise in serverless, event-driven architectures and generative AI to its work with clients. As a solutions architect, he partners with independent software vendors to reimagine their products for the cloud era – from modernizing legacy systems to embedding AI capabilities that differentiate their offerings. Sparsh believes that the best solutions emerge from understanding both the technical possibilities and the business context.
 Heiki Park Principal Solutions Architect at AWS. In his 9+ years at AWS, he has helped enterprise customers rethink how to build and operate cloud-native applications, adopt serverless and event-driven patterns, and build practical generative AI applications. Heiki is an avid runner and enjoys analyzing activity data to measure improvements in cardiovascular fitness.
Heiki Park Principal Solutions Architect at AWS. In his 9+ years at AWS, he has helped enterprise customers rethink how to build and operate cloud-native applications, adopt serverless and event-driven patterns, and build practical generative AI applications. Heiki is an avid runner and enjoys analyzing activity data to measure improvements in cardiovascular fitness.
 Dhaval Patel Principal Generative AI Tech Lead at AWS. He has worked with organizations ranging from large enterprises to medium-sized startups on problems related to agentic AI, deep learning, and distributed computing.
Dhaval Patel Principal Generative AI Tech Lead at AWS. He has worked with organizations ranging from large enterprises to medium-sized startups on problems related to agentic AI, deep learning, and distributed computing.