Python dominates AI and machine learning for a simple reason: its ecosystem is amazing. Most projects are built on a small set of libraries that handle everything from large-scale data loading to deep learning. Knowing these libraries makes the entire development process faster and easier.
Let’s break them down into one practical order. Starting with the basics, then moving into AI and concluding with Machine Learning.
Core Data Science Library
These are not negotiable. If you touch data, you use them. Your fundamentals in AI/ML depend on being familiar with these.
1. NumPy – Numerical Python
This is really where it all starts. If Python is the language, then NumPy is the math brain behind it.
Why? Python lists are heterogeneous datatypes, which causes variations in built-in type checking When any operation is done on them. Numerical lists are homogeneous! Meaning the data type is defined during initialization, skipping type checking and allowing faster operation.
used for:
- vectorized mathematics
- linear algebra
- random sampling
Almost every serious ML or DL library relies on NumPy quietly doing fast array math in the background.
Install using: pip install numpy
2. Panda – Panel Data
Pandas is what turns messy data into something you can reason about. It feels like Excel on steroids, but with actual logic and reproducibility instead of dumb human errors. Pandas especially shines when it is used to process huge datasets.
used for:
- data cleaning
- feature engineering
- aggregation and addition
It allows efficient manipulation, cleaning and analysis of structured, tabular or time-series data.
Install using: pip install pandas
3. SciPy – Scientific Python
When is SciPy for? NumPy alone is not enough. It gives you massive scientific tools that show up in real problems, from optimization to signal processing and statistical modeling.
used for:
- Adaptation
- figures
- signal processing
Ideal for those who want to have scientific and mathematical work in one place.
Install using: pip install scipy
artificial intelligence library
This is where neural networks live. The basic principles of data science will be built from these.
4.TensorFlow – Tensor Flow
Google’s end-to-end deep learning platform. TensoFlow is built for those times when your models need to leave your laptop and survive in the real world. It is thoughtful, structured and designed for deploying models at serious scale.
used for:
- Nervous system
- training delivered
- model deployment
For those looking for a strong ecosystem on artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Install using: pip install tensorflow
5. PyTorch – Python Torch
META’s research-first framework. PyTorch is more like writing general Python for training neural networks. This is why researchers love it: less abstraction, more control, and less fighting with the framework.
used for:
- research prototype
- custom architecture
- Use
Perfect for those who want to ease their way into AI.
Install using: pip install torch
6. OpenCV – Open Source Computer Vision
Machines start seeing the world with OpenCV. It handles all the important details of images and videos so you can focus on high-level vision problems instead of pixel math.
used for:
- facial recognition
- object tracking
- image processing pipeline
One-stop for image processing enthusiasts who want to integrate it with machine learning.
Install using: pip install cv2
machine learning library
This is where models start being made.
7. Scikit-Learn – Scientific Kit for Learning
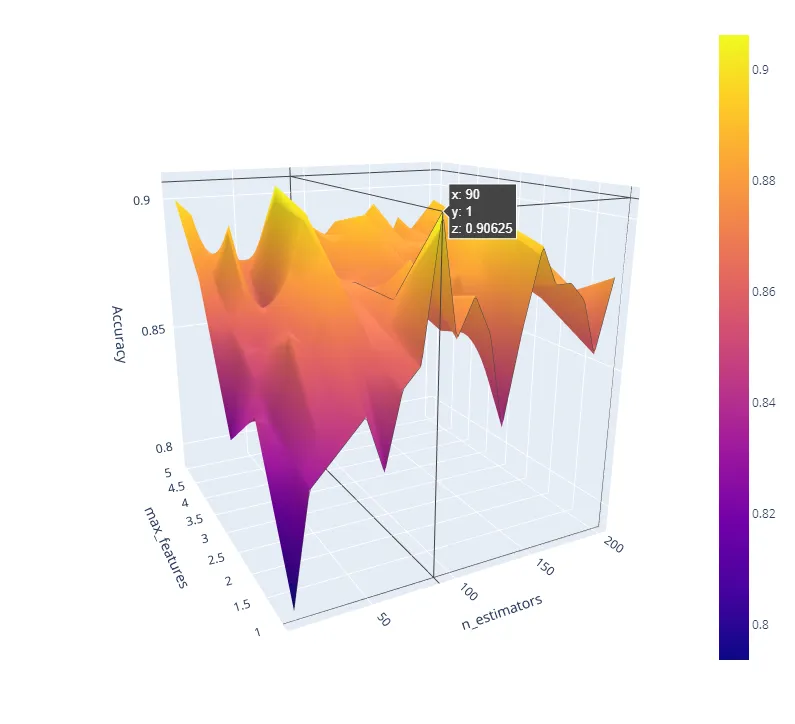
Scikit-learn is the library that teaches you what machine learning really is. Clean API, lots of algorithms, and enough abstractions to learn without hiding how things work.
used for:
- classification
- Return
- clustering
- model evaluation
For ML learners who want seamless integration with the Python data science stack, Scikit-Learn is a preferred choice.
Install using: pip install scikit-learn
8. XGBoost – Extreme gradient boosting
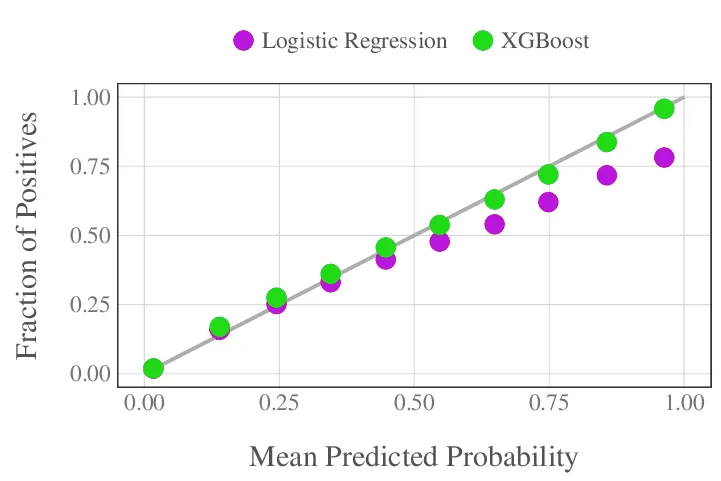
XGBoost is the reason why neural networks do not automatically win on tabular data. It is extremely effective, optimized and still one of the most robust baselines in real-world ML.
used for:
- tabular data processing
- structured prediction
- attribute importance identification
For model trainers who want exceptional speed and built-in regularization to prevent overfitting.
Install using: pip install xgboost
9. LightGBM – Light gradient boosting machine
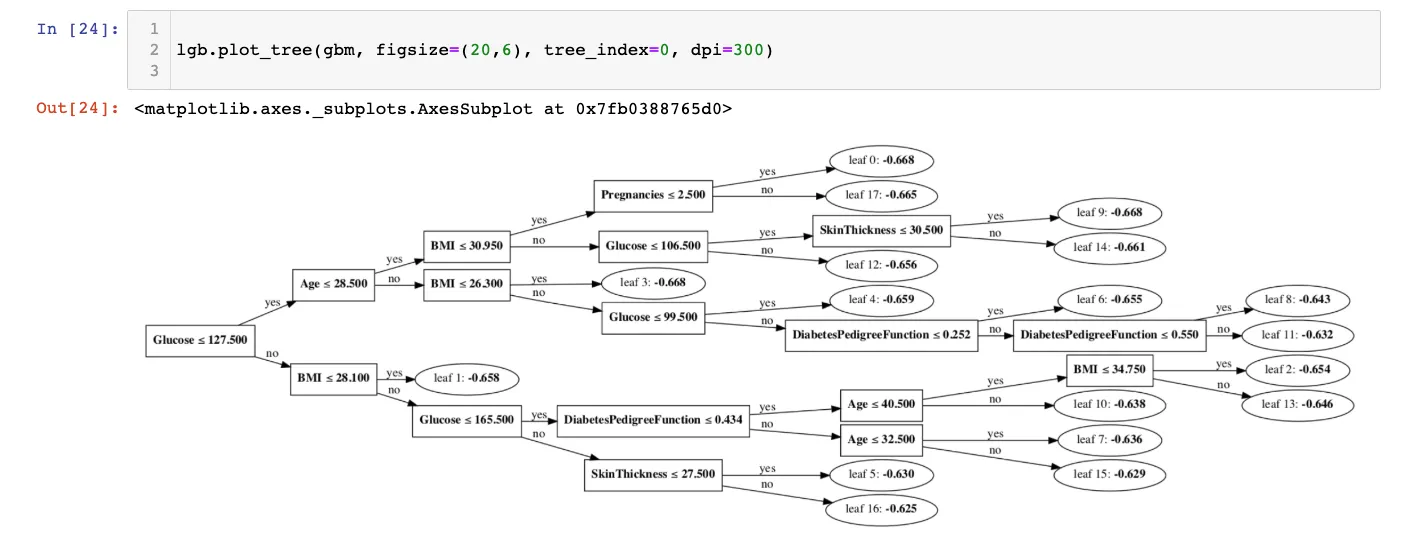
Fast alternative to Microsoft’s XGBoost. LightGBM exists when XGBoost starts to feel slow or heavy. It is designed for speed and memory efficiency, especially when your dataset is huge or high-dimensional.
used for:
- high-dimensional data processing
- low latency training
- massive ml
For those who want to boost XGBoost.
Install using: pip install lightgbm
10. CatBoost – Hierarchical Boosting

CatBoost is what you reach for when hierarchical data becomes a pain. It handles categories intelligently out of the box, so you spend less time encoding and more time modeling.
used for:
- Hierarchical-heavy dataset
- minimal feature engineering
- strong basic model
Install using: pip install cat boost
final take
It would be hard to come up with an AI/ML project without previous libraries. Every serious AI engineer eventually touches all 10. The typical learning path of the previously mentioned Python libraries looks like this:
Panda → numpy → scikit-learn → XGBoost → pytorch → tensorflow
This process assures that learning ranges from basics to advanced frameworks that are built using it. But it is not descriptive in any way. You can choose whatever order suits you or choose one of these libraries depending on your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Start with Pandas and NumPy, then move to Scikit-Learn before touching deep learning libraries.
A. PyTorch is preferred for research and experimentation, while TensorFlow is built for production and large-scale deployment.
A. Use CatBoost when your dataset has many categorical features and you want minimal preprocessing.
Login to continue reading and enjoy expertly curated content.

